TL;DR: Discourse = language in a real situation (who speaks, to whom, where, why, and with what effect).
Discourse analysis = a practical way to unpack how meaning is created beyond words: intention, tone, roles, background knowledge, power, setting—everything that makes the same sentence mean different things.
A one-minute story
You tell a developer: “You did great.”
- At school, the same phrase once sounded like a throwaway line—“ok, whatever”—and caused irritation.
- In your work relationship now, it signals trust and professional respect.
Same words. Different situation. Different effect.
That gap between words and effect—that’s where discourse lives.
Text vs Discourse vs Discourse Analysis
| Layer | Core question | What you actually look at | Typical outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Текст | What was said? | Words, grammar, punctuation | Literal meaning |
| Discourse | Who said it, to whom, where, for what purpose? | Roles, relationships, goals, norms, power, channel (email, call, TV), timing | Intended meaning in context |
| Discourse analysis | How exactly does this meaning get built? | Word choice, register, tone, presuppositions, cultural background, what’s said vs implied vs achieved | Actionable insight: how to say/translate so it lands right |
The three moves behind any message (speech-act lens)
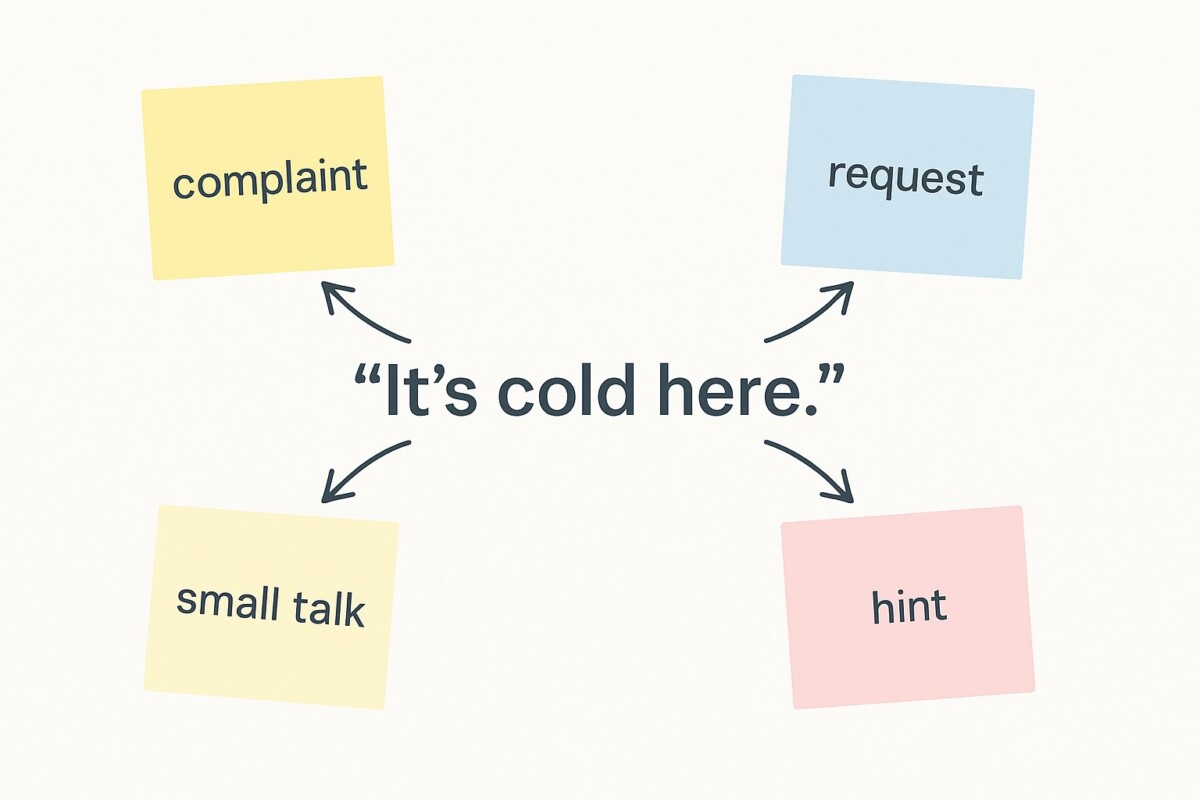
- Locution — the literal words. “It’s cold here.”
- Illocution — the intention behind them. A request to close the window (not meteorology).
- Perlocution — the effect on the listener. The person actually closes the window (or gets annoyed…).
Everyday abbreviations you’ll meet (and mix up)
- CTA — Call to Action
A line or button in marketing that asks the user to do something.
Examples: “Sign up now,” “Book your lesson,” “Click here.” - CTO — Chief Technology Officer
A job title. This is the senior executive responsible for a company’s tech strategy.
Do not confuse it with CTA!
In discourse, context shows which one is meant:
- “We need a stronger CTA in this ad” → marketing phrase.
- “Our CTO approved the new platform” → person/job title.
Why learners and translators keep tripping over discourse
- Right word, wrong world — correct vocabulary, wrong tone/register.
- I said it… they didn’t hear it — failure of alignment, not grammar.
- Tone drift — “Could you…?” in English ≠ same politeness in German, Russian, Ukrainian.
The 7-point Discourse Checklist
- Goal — what should the listener do/feel/decide?
- Audience — age, status, expertise, sensitivity.
- Relationship — close vs formal, equal vs hierarchical.
- Setting & channel — classroom, WhatsApp, Zoom, public/private.
- Register & tone — formal, friendly, ironic, firm?
- Cultural code — what signals politeness or credibility here?
- Likely effect — what if they misread? Adjust words to steer effect.
Translation Lab: from words → effect
Source line: “We’ll consider your request.”
- Could mean: genuine promise, polite refusal, delay tactic.
- Translation choices (EN → DE/UA/RU):
- German (neutral promise): Wir prüfen Ihre Anfrage sorgfältig und melden uns bis Freitag.
- Ukrainian (soft refusal): Ми розглянемо ваше звернення, але зараз не можемо обіцяти рішення.
- Russian (clear next step): Мы внимательно изучим запрос и дадим ответ до пятницы.
Where the term comes from
- Austin & Searle (philosophy of language): speech acts = intention + effect.
- Pragmatics & linguistics: context shapes meaning.
- Sociology (Foucault): discourse as power and norms.
- Applied linguistics: everyday toolkit for teachers, translators, managers.
Why this matters for you
- Learners: you don’t just learn words; you learn how to be understood.
- Translators: you don’t carry words across languages, you carry effects.
- Professionals: your message succeeds only if the intended action really happens.
How we teach this
За адресою Levitin Language School / Стартова мовна школа Тимура Левітіна we focus on:
- Meaning first → 2. Audience lens → 3. Language choices → 4. Effect check → 5. Cross-language transfer.
Глобальне навчання. Персональний підхід.
Quick practice
- Rephrase politely, firmly, formally.
- Add intention: “Reminder about tomorrow” → “…please confirm attendance.”
- Translate the ефект, not just the word.
Summary
Discourse = language in real use.
Discourse analysis = the toolkit to understand and shape meaning.
It’s not academic decoration. It’s the operating system of communication.
Further reading
- Shall in Business English: obligation, promise, or nothing at all?
- By vs Until vs Through: legal & business realities across languages
- Present Simple vs Present Continuous — easy guide with examples
- Our US blog
Contacts
- 🌍 Main site: https://levitinlanguageschool.com
- 🌎 US site: https://languagelearnings.com
- Telegram: @START_SCHOOL_TYMUR_LEVITIN
- WhatsApp/Viber: +380 93 291 34 29
🖊️ Author’s development: Tymur Levitin — founder, director, lead teacher and translator, Levitin Language School / Стартова мовна школа Тимура Левітіна.
© Тимур Левітін. Всі права захищені.